Mataupu
Medical treatments for a herniated disc
Togafitiga o faʻasolosolo solo mainly involves a focus malolo, renouncing risky behaviors for the back and taking Foma'i to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. In the majority of cases, these measures are sufficient to reduce symptoms and heal the herniated disc. In fact, approximately 60% of affected people respond well to these treatments in 1 week, and 90% in less than 6 weeks. The tīpiga is rarely needed.
Malolo le tua
Le malolo moega can be useful for 1 day or 2 maximum in phase of acute pain. It is however preferable not to prolong this rest beyond 1 or 2 days and to resume its activities as soon as possible. Inaction and stillness can causeatrophy maweakened back muscles and compromise the normal mobility of the joints of the lumbar spine.
Medical treatments for a herniated disc: understand everything in 2 minutes
le avanoa that best support the lumbar spine are:
- lying on your side, knees bent, a pillow under the head and another between the knees (pregnant women can add a pillow under their belly);
- laying on the back, e aunoa ma se aluga i lalo o le ulu, ma se tasi pe sili atu aluga i lalo o tulivae ma se solo taai poʻo se tamaʻi aluga i le omo o le pito i lalo.
During the first few days, ice applications at the spine, near the hernia, help reduce pain (but not inflammation, lodged too deeply). Subsequently, it is suggested to apply vevela or take hot baths.
Foma'i
For temporary pain control over a short period of time (usually 7 to 10 days, occasionally 2 to 3 weeks, but rarely more), drugs are usually taken. analgesics (acetaminophen: Tylenol® or acetylsalicylic acid: Aspirin®), aneti-inflammatory (such as ibuprofen: Advil®, Motrin®, for example) or musika malolo (Robaxacet®). If the pain is intense and persistent, the doctor may prescribe more powerful painkillers such as narcotics, or higher doses of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Faamatalaga. E taua lena fafine maitaga consult their doctor before taking any of these medications.
Drugs by injection. To overcome persistent pain, epidural injections of corticosteroids oranalgesics are sometimes prescribed. THE’injection d’enzymes (chymopapain) in the intervertebral disc can also be done. The enzymes destroy the protruding portion of the disc that compresses the nerve, preventing surgery. On the other hand, enzymes tend to be used less because they can cause severe allergic reactions.
Fomaʻi togafitiga
Once the symptoms have eased, the doctor may prescribe sessions of fetuunaiga in order to speed up complete healing. These are mainly exercises that improve posture, strengthen the muscles of the back and abdomen and make the body more flexible.
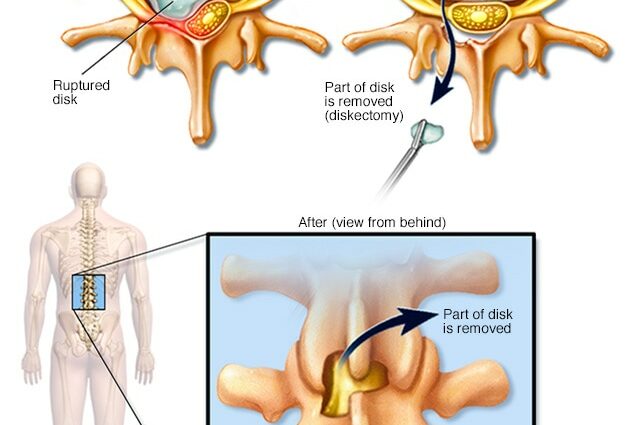
tīpiga
le surgical treatments are used if the pain persists and is bothersome, if there is persistent muscle weakness in an arm, leg, toe, etc., or if you have more severe symptoms.
Surgery removes the pressure that the intervertebral disc exerts on the nerve roots. Different techniques are used. The discectomie consists of completely or partially removing the intervertebral disc. This operation can also be performed laparoscopically: it is the microdiscectomy. This less invasive technique requires only a small incision in the skin. It is commonly used in the United States, but still little in Quebec. The 2 types of surgeries give similar results.
The surgery involves nisi tulaga lamatia : get an infection, injure a nerve, have fibrous scars, or put stress on other vertebrae.