Definition of electroencephalogram
LEelemenephalogram (or EEG) is an examination that measures theelectrical activity of the brain. In reality, the examination is called electroencephalography and the electroencephalogram denotes the transcription of the recording as a trace. It allows to study and differentiate the main types of brain waves (delta, theta, alpha and beta).
This painless test is primarily used to diagnoseepilepsy.
Why have an electroencephalogram?
The electroencephalogram can detect several faaletonu neura, in connection with anomalies of thefaiʻai galue.
This examination is especially prescribed in case of suspicion of epilepsy. It is also used:
- To take stock of a fa'alavelave fa'afuase'i
- To accurately diagnose the type of epilepsy syndrome and monitor its treatment
- i cas o coma or state of confusion
- pe a uma a ta
- e su'esu'e le lelei o le moe po'o le su'esu'eina a maʻi moe (sleep apnea syndrome, etc.)
- e faʻamaonia le oti fai'ai
- e iloa ai a encephalitis (Creutzfeld-Jacob, hepatic encephalopathy).
The examination is generally carried out in a waking state. The patient is lying in a reclining chair, in the hospital, clinic or doctor’s office. His head is resting on a foam cushion.
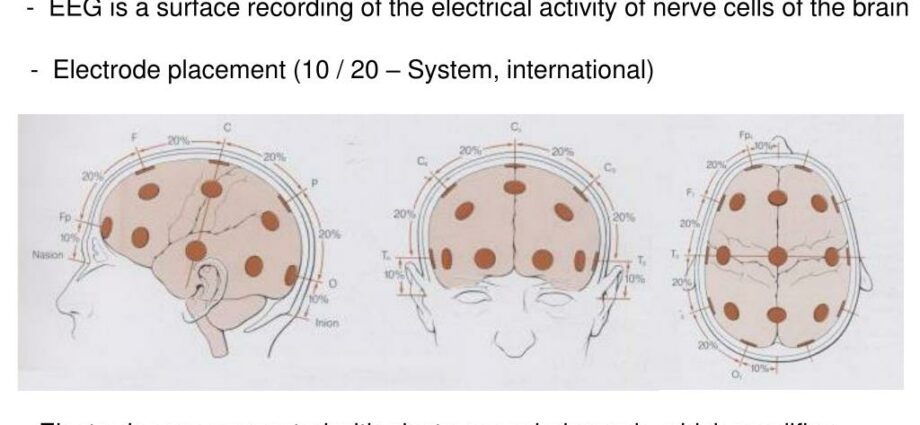
The medical staff place electrodes on the scalp (between 8 and 21), according to a very precise position. They are fixed using an adhesive conductive paste. The skin of the skull is first wiped with an alcohol swab.
The recording lasts about twenty minutes. It can also be done after sleep deprivation or for longer periods of time, up to 24 hours. It is important to remain calm and still during the exam.
In some cases, anomalies are “triggered”:
- asking the patient to breathe fast and hard (hyperpnea test) for about three minutes
- by exposing it to intermittent light stimulation (SLI), i.e. intermittent flashes with a stroboscopic effect, which can trigger an epileptic seizure or reveal EEG abnormalities
Shampoo is done after the examination to remove the adhesive paste.
What results can we expect from an electroencephalogram?
Several abnormalities in the electrical activity of the brain can be detected using EEG.
In epilepsy, for example, the examination will confirm the diagnosis and monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.
The doctor may offer appropriate treatment and possibly prescribe other examinations, such as a Fai'ai MRI.
Faitau foi: O le a le ma'i epileptic? Our coma file Learn more about stroke |